Women’s health encompasses a broad spectrum of conditions that uniquely or disproportionately affect females. Awareness of these prevalent diseases is crucial for early detection, effective management, and prevention. Below is an in-depth exploration of the ten most common diseases among women, including their prevalence, consequences, and the bodily systems they impact.
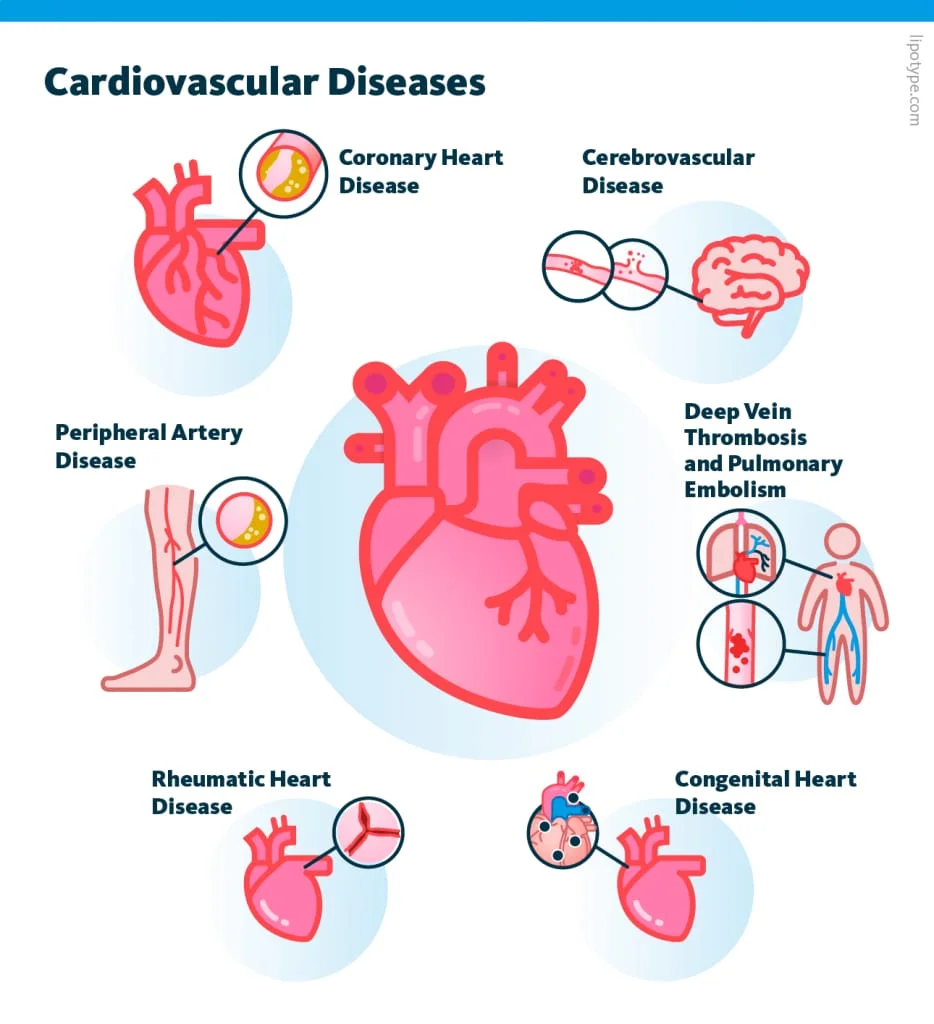
1. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD)
Prevalence: Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death among women globally.
Consequences: CVD can lead to heart attacks, strokes, and other serious complications.
Affected Systems: Primarily impacts the circulatory system, including the heart and blood vessels.
Note: Women may experience different symptoms than men, such as shortness of breath, nausea, and back or jaw pain.
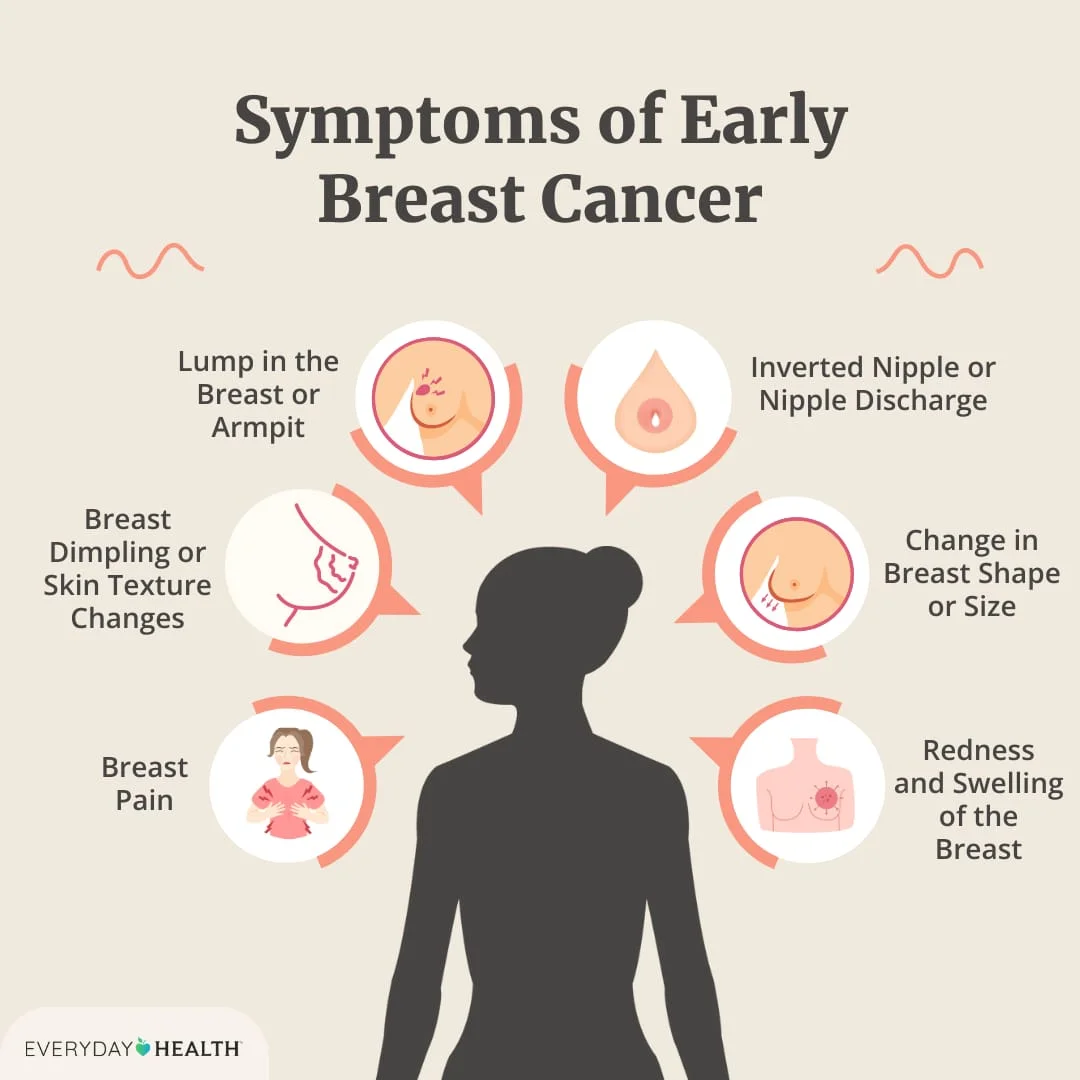
2. Breast Cancer
Prevalence: Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting women worldwide.
Consequences: If not detected early, it can spread to other parts of the body, leading to severe health issues and death.
Affected Systems: Primarily affects the mammary glands but can metastasize to other organs.
Note: Regular mammograms and self-examinations are vital for early detection.
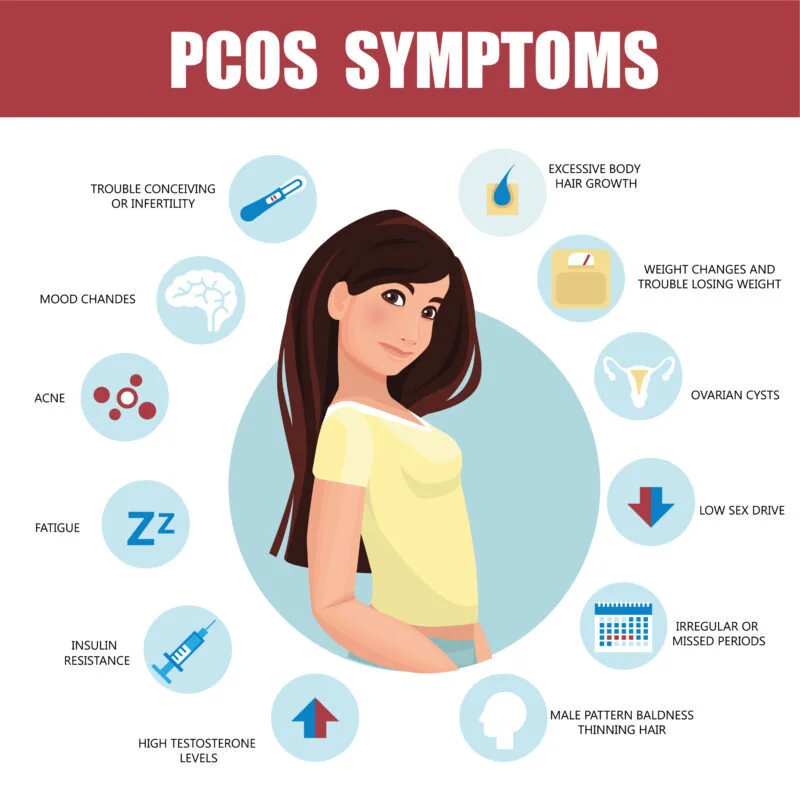
3. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Prevalence: PCOS affects approximately 5-10% of women of childbearing age.
Consequences: Can lead to infertility, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease.
Affected Systems: Endocrine system and reproductive organs.
Note: Symptoms include irregular periods, excessive hair growth, acne, and obesity.
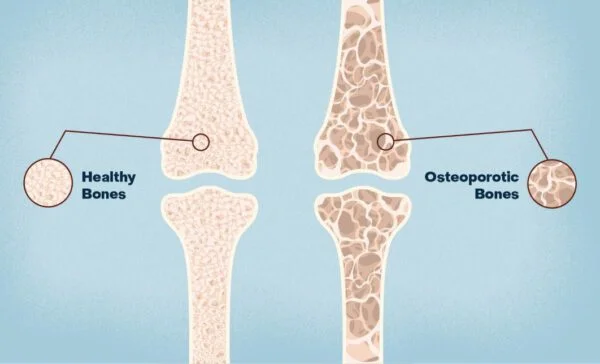
4. Osteoporosis
Prevalence: Common among postmenopausal women due to decreased estrogen levels.
Consequences: Increased risk of fractures, particularly in the hip, spine, and wrist.
Affected Systems: Skeletal system.
Note: Adequate calcium intake and weight-bearing exercises are preventive measures.
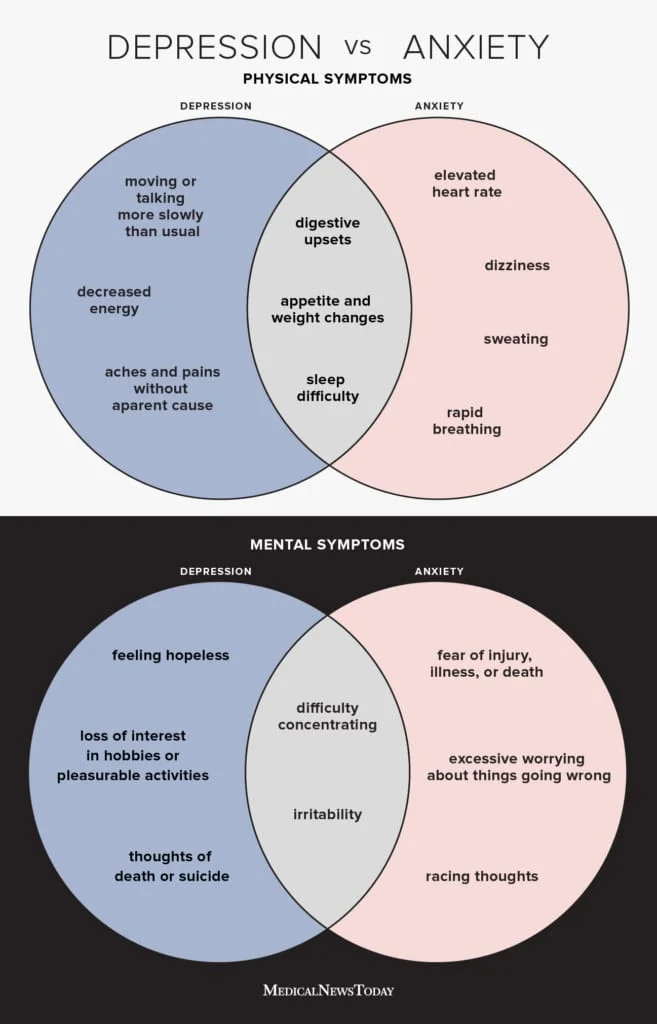
5. Depression and Anxiety
Prevalence: Women are more likely than men to experience depression and anxiety disorders.
Consequences: It can impair daily functioning and increase the risk of suicide.
Affected Systems: Nervous system and mental health.
Note: Hormonal fluctuations, societal pressures, and life events contribute to higher prevalence.
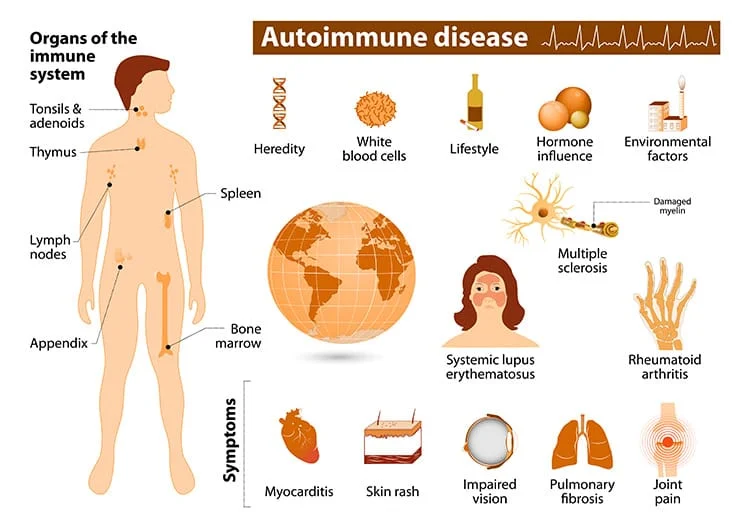
6. Autoimmune Diseases
Prevalence: Approximately 78% of individuals with autoimmune diseases are women.
Consequences: Varies by disease; can lead to organ damage and systemic issues.
Affected Systems: Immune system; specific organs depending on the disease (e.g., thyroid in Hashimoto’s).
Note: Common autoimmune diseases in women include lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis.
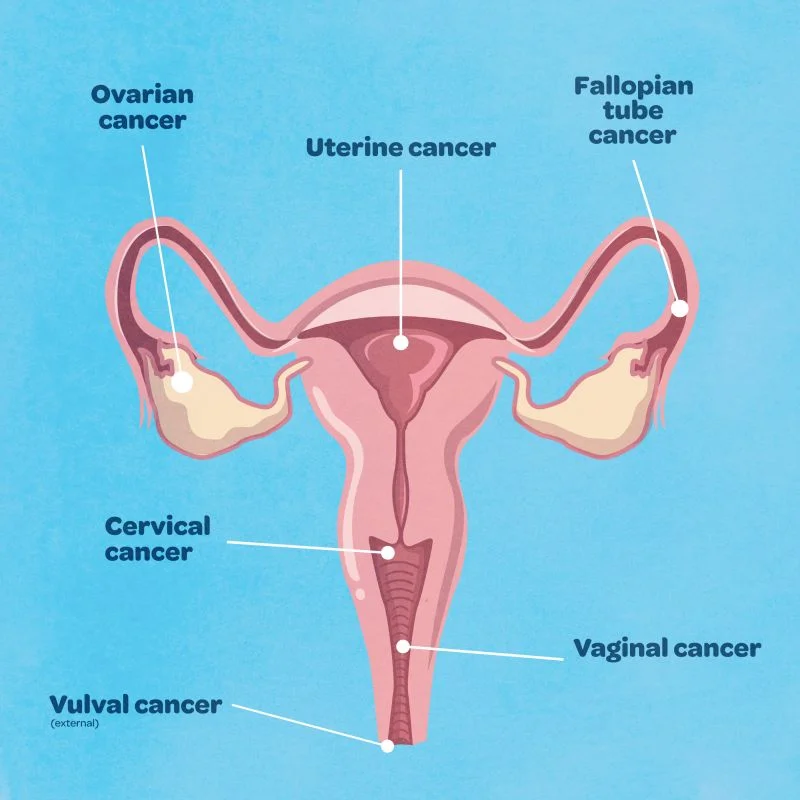
7. Cervical and Ovarian Cancers
Prevalence: Cervical cancer is the fourth most common cancer in women globally.
Consequences: Can be fatal if not detected and treated early.
Affected Systems: Reproductive system.
Note: Regular Pap smears and HPV vaccinations are crucial for prevention.
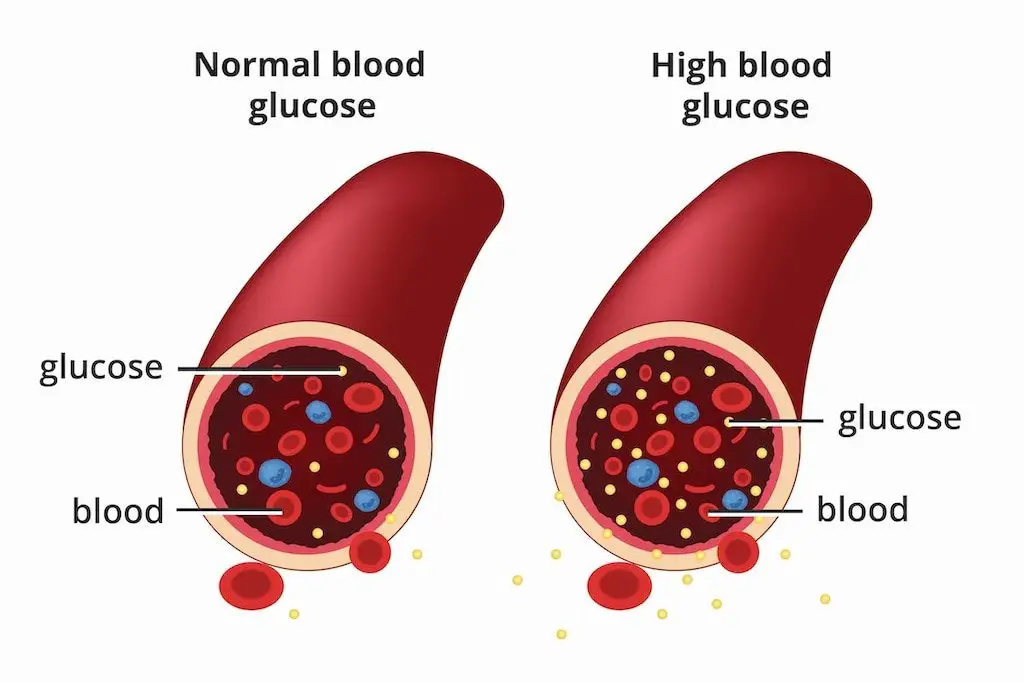
8. Diabetes Mellitus
Prevalence: Type 2 diabetes is increasingly common among women, especially with rising obesity rates.
Consequences: Can lead to cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, and neuropathy.
Affected Systems: Endocrine system and multiple organ systems.
Note: Gestational diabetes during pregnancy increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
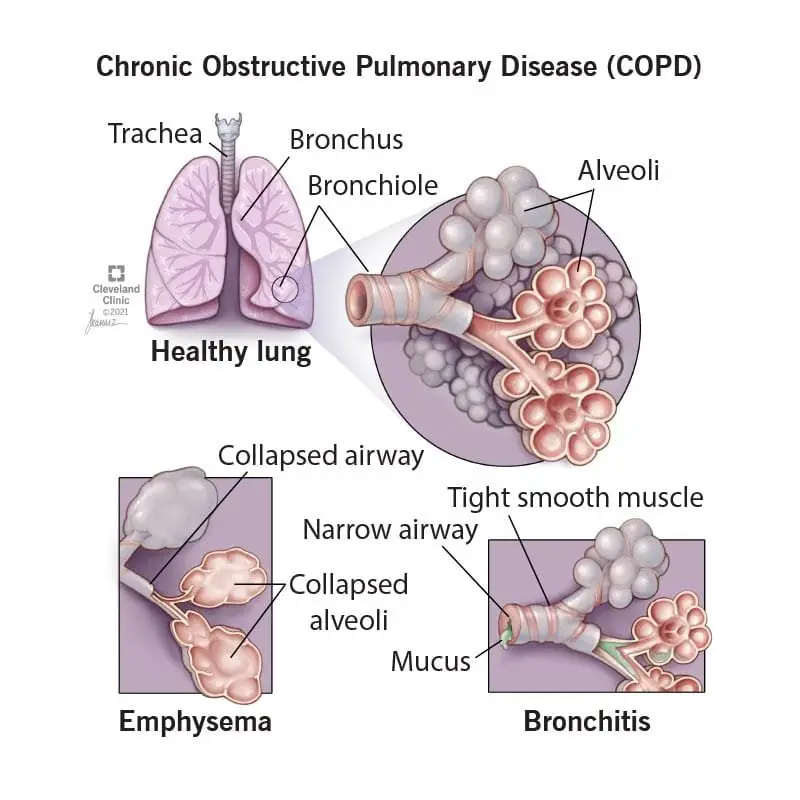
9. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Prevalence: Rising among women, partly due to increased smoking rates.
Consequences: Causes breathing difficulties and can lead to respiratory failure.
Affected Systems: Respiratory system.
Note: Smoking cessation is the most effective preventive measure.

10. Endometriosis
Prevalence: Affects approximately 10% of women of reproductive age.
Consequences: It can cause chronic pelvic pain and infertility.
Affected Systems: Reproductive system.
Note: Often underdiagnosed; awareness and medical consultation are essential.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the early signs of cardiovascular disease in women?
Early signs include fatigue, shortness of breath, nausea, and chest discomfort.
2. How often should women get screened for breast cancer?
Women aged 50 to 74 should have mammograms every two years; those with higher risk factors may need earlier and more frequent screenings.
3. Can lifestyle changes reduce the risk of developing osteoporosis?
Yes, regular weight-bearing exercise and adequate calcium and vitamin D intake can help maintain bone density.
4. Are there effective treatments for PCOS?
While there’s no cure, symptoms can be managed with lifestyle changes, medications, and hormonal therapies.
5. How does depression manifest differently in women?
Women may experience more pronounced feelings of guilt, worthlessness, and fatigue compared to men.
6. What autoimmune diseases are most common in women?
Lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis are prevalent among women.
7. Is cervical cancer preventable?
Yes, through regular Pap smear examinations.

